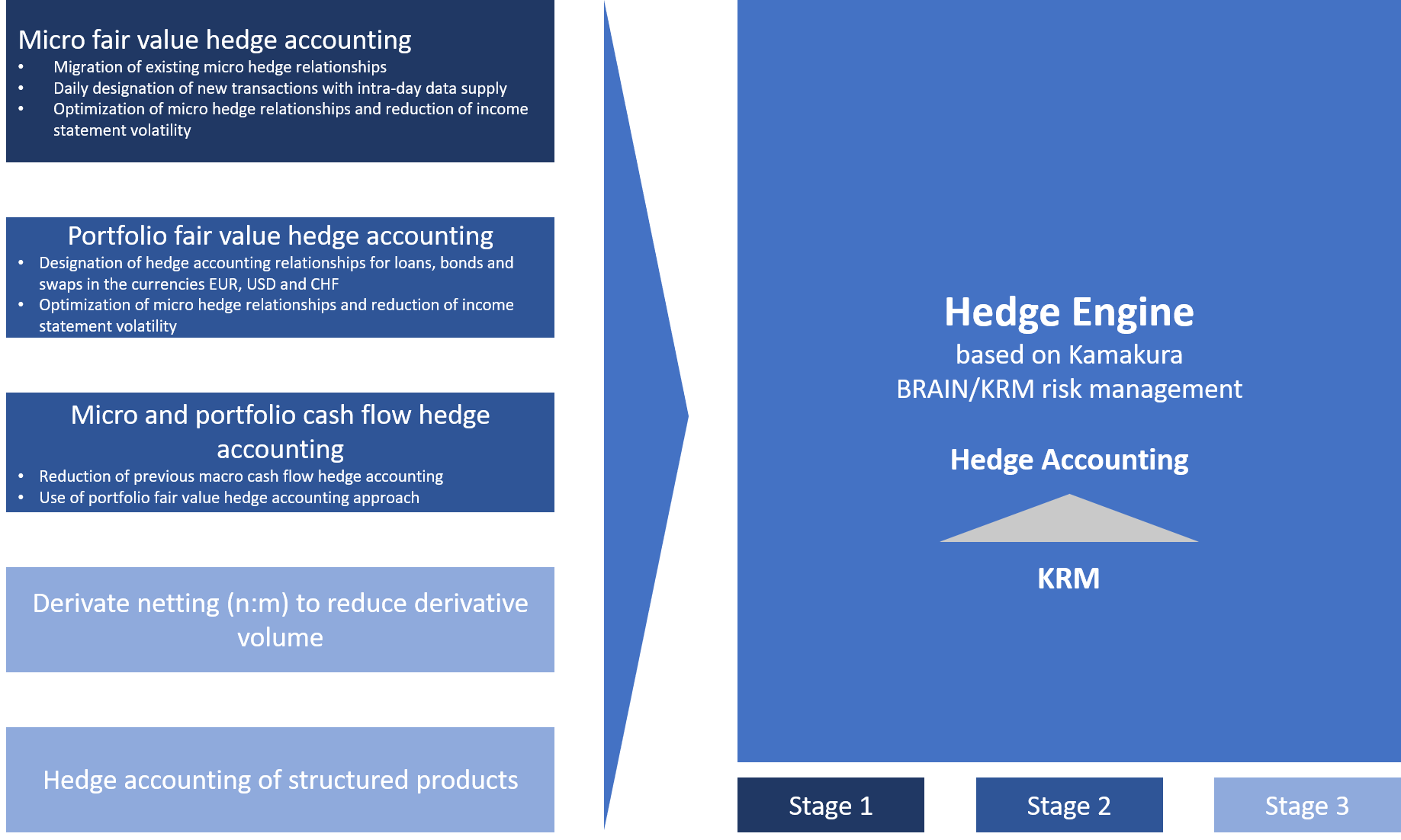
Together with zeb RBI implemented the Hedge Engine in a three-stage process to apply additional hedge accounting methods of portfolio fair value hedge accounting and to continue the optimization process.
The first and second stage of the hedge accounting introduction lasted nine months and were followed by additional four months for extended hedge methods as part of stage 3. The run-up and project setup concentrated on defining business requirements and analyzing data requirements. This was then used to derive the target architecture in view of possible implementation options. To be able to estimate balance sheet and income statement effects with the implementation of the Hedge Engine, test calculations were conducted for micro and portfolio fair value hedge accounting. Stage 1 dealt with creating the business concept which was used as the basis for implementing the Hedge Engine. This allowed for the migration of existing micro fair value hedges to the software and designation of new micro fair value hedge relationships. Stage 2 focused on introducing portfolio fair value hedge accounting and cash flow hedge accounting, as well as the “Hedge Selection” module which is part of the Hedge Engine. Consequently, the income statement impact was improved through optimized assignments to hedge accounting approaches based on treasury interest rate risk management. The hedge accounting enhancements of stage 3 included the introduction of micro fair value hedge accounting for structured products and the introduction of a regression analysis method based on prospective cash flows, which also led to an improved hedge effectiveness. Furthermore, the project team developed and implemented a prototype for derivative netting (n:m).